一、Fork/Join 框架简介
Fork/Join 它可以将一个大的任务拆分成多个子任务进行并行处理,最后将子任务结果合并成最后的计算结果,并进行输出。Fork/Join 框架要完成两件事情:
Fork:把一个复杂任务进行分拆,大事化小
Join:把分拆任务的结果进行合并
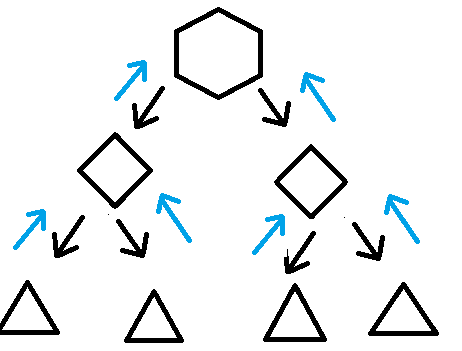
- 任务分割:首先 Fork/Join 框架需要把大的任务分割成足够小的子任务,如果子任务比较大的话还要对子任务进行继续分割
- 执行任务并合并结果:分割的子任务分别放到双端队列里,然后几个启动线程分别从双端队列里获取任务执行。子任务执行完的结果都放在另外一个队列里,启动一个线程从队列里取数据,然后合并这些数据。
在 Java 的 Fork/Join 框架中,使用两个类完成上述操作
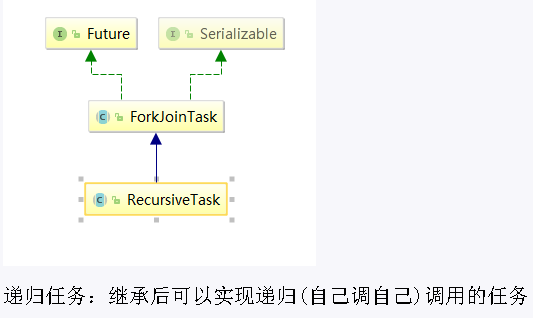
- ForkJoinTask: 我们要使用 Fork/Join 框架,首先需要创建一个 ForkJoin 任务。该类提供了在任务中执行 fork 和 join 的机制。通常情况下我们不需要直接集成 ForkJoinTask 类,只需要继承它的子类,Fork/Join 框架提供了两个子类:
- RecursiveAction:用于没有返回结果的任务
- RecursiveTask: 用于有返回结果的任务
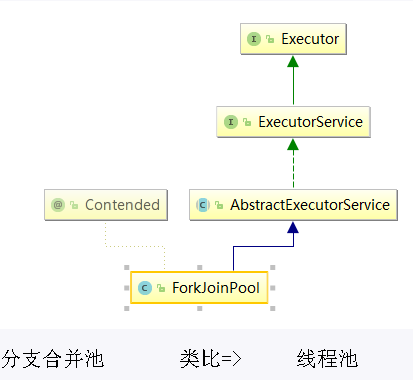
- ForkJoinPool: ForkJoinTask 需要通过 ForkJoinPool 来执行
- RecursiveTask: 继承后可以实现递归(自己调自己)调用的任务
Fork/Join 框架的实现原理
ForkJoinPool 由 ForkJoinTask 数组和 ForkJoinWorkerThread 数组组成,ForkJoinTask 数组负责将存放以及将程序提交给 ForkJoinPool,而ForkJoinWorkerThread 负责执行这些任务。
二、Fork 方法
Fork 方法的实现原理: 当我们调用 ForkJoinTask 的 fork 方法时,程序会把任务放在 ForkJoinWorkerThread 的 pushTask 的 workQueue 中,异步地执行这个任务,然后立即返回结果.
/**
* Arranges to asynchronously execute this task in the pool the
* current task is running in, if applicable, or using the {@link
* ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} if not {@link #inForkJoinPool}. While
* it is not necessarily enforced, it is a usage error to fork a
* task more than once unless it has completed and been
* reinitialized. Subsequent modifications to the state of this
* task or any data it operates on are not necessarily
* consistently observable by any thread other than the one
* executing it unless preceded by a call to {@link #join} or
* related methods, or a call to {@link #isDone} returning {@code
* true}.
*
* @return {@code this}, to simplify usage
*/
public final ForkJoinTask<V> fork() {
Thread t;
if ((t = Thread.currentThread()) instanceof ForkJoinWorkerThread)
((ForkJoinWorkerThread)t).workQueue.push(this);
else
ForkJoinPool.common.externalPush(this);
return this;
}pushTask 方法把当前任务存放在 ForkJoinTask 数组队列里。然后再调用ForkJoinPool 的 signalWork()方法唤醒或创建一个工作线程来执行任务。代码如下:
/**
* Pushes a task. Call only by owner in unshared queues.
*
* @param task the task. Caller must ensure non-null.
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if array cannot be resized
*/
final void push(ForkJoinTask<?> task) {
ForkJoinTask<?>[] a;
int s = top, d, cap, m;
ForkJoinPool p = pool;
if ((a = array) != null && (cap = a.length) > 0) {
QA.setRelease(a, (m = cap - 1) & s, task);
top = s + 1;
if (((d = s - (int)BASE.getAcquire(this)) & ~1) == 0 &&
p != null) { // size 0 or 1
VarHandle.fullFence();
p.signalWork();
}
else if (d == m)
growArray(false);
}
}三、join 方法
Join 方法的主要作用是阻塞当前线程并等待获取结果。让我们一起看看 ForkJoinTask 的 join 方法的实现,代码如下:
/**
* Returns the result of the computation when it
* {@linkplain #isDone is done}.
* This method differs from {@link #get()} in that abnormal
* completion results in {@code RuntimeException} or {@code Error},
* not {@code ExecutionException}, and that interrupts of the
* calling thread do <em>not</em> cause the method to abruptly
* return by throwing {@code InterruptedException}.
*
* @return the computed result
*/
public final V join() {
int s;
if (((s = doJoin()) & ABNORMAL) != 0)
reportException(s);
return getRawResult();
}它首先调用 doJoin 方法,通过 doJoin()方法得到当前任务的状态来判断返回什么结果,任务状态有 4 种:
已完成(NORMAL)、被取消(CANCELLED)、信号(SIGNAL)和 出现异常(EXCEPTIONAL)
- 如果任务状态是已完成,则直接返回任务结果。
- 如果任务状态是被取消,则直接抛出 CancellationException
- 如果任务状态是抛出异常,则直接抛出对应的异常
分析一下 doJoin 方法的实现
/**
* Implementation for join, get, quietlyJoin. Directly handles
* only cases of already-completed, external wait, and
* unfork+exec. Others are relayed to ForkJoinPool.awaitJoin.
*
* @return status upon completion
*/
private int doJoin() {
int s; Thread t; ForkJoinWorkerThread wt; ForkJoinPool.WorkQueue w;
return (s = status) < 0 ? s :
((t = Thread.currentThread()) instanceof ForkJoinWorkerThread) ?
(w = (wt = (ForkJoinWorkerThread)t).workQueue).
tryUnpush(this) && (s = doExec()) < 0 ? s :
wt.pool.awaitJoin(w, this, 0L) :
externalAwaitDone();
}
/**
* Primary execution method for stolen tasks. Unless done, calls
* exec and records status if completed, but doesn't wait for
* completion otherwise.
*
* @return status on exit from this method
*/
final int doExec() {
int s; boolean completed;
if ((s = status) >= 0) {
try {
completed = exec();
} catch (Throwable rex) {
completed = false;
s = setExceptionalCompletion(rex);
}
if (completed)
s = setDone();
}
return s;
}在 doJoin()方法流程如下:
- 首先通过查看任务的状态,看任务是否已经执行完成,如果执行完成,则直接返回任务状态;
- 如果没有执行完,则从任务数组里取出任务并执行。
- 如果任务顺利执行完成,则设置任务状态为 NORMAL,如果出现异常,则记录异常,并将任务状态设置为 EXCEPTIONAL。
四、Fork/Join 框架的异常处理
ForkJoinTask 在执行的时候可能会抛出异常,但是我们没办法在主线程里直接捕获异常,所以 ForkJoinTask 提供了 isCompletedAbnormally() 方法来检查任务是否已经抛出异常或已经被取消了,并且可以通过 ForkJoinTask 的 getException 方法获取异常。
getException 方法返回 Throwable 对象,如果任务被取消了则返回 CancellationException。如果任务没有完成或者没有抛出异常则返回 null。
五、入门案例
场景: 生成一个计算任务,计算 1+2+3………+100 每 10 个数切分一个子任务
class MyTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {
//拆分差值不能超过10,计算10以内运算
private static final Integer VALUE = 10;
private int begin ;//拆分开始值
private int end;//拆分结束值
private int result ; //返回结果
//创建有参数构造
public MyTask(int begin,int end) {
this.begin = begin;
this.end = end;
}
//拆分和合并过程
protected Integer compute() {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", begin: " + begin + ", end: " + end);
//判断相加两个数值是否大于10
if((end-begin)<=VALUE) {
//相加操作
for (int i = begin; i <=end; i++) {
result = result+i;
}
} else {// 递归调用,切分为 2 个小任务
//获取中间值
int middle = (begin+end)/2;
//拆分左边
MyTask task01 = new MyTask(begin,middle);
//拆分右边
MyTask task02 = new MyTask(middle+1,end);
// 执行:异步
task01.fork();
task02.fork();
// 同步阻塞获取执行结果
result = task01.join()+task02.join();
}
return result;
}
}
public class ForkJoinDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建MyTask对象
MyTask myTask = new MyTask(0,100);
//创建分支合并池对象
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Integer> forkJoinTask = forkJoinPool.submit(myTask);
//获取最终合并之后结果
Integer result = forkJoinTask.get();
System.out.println(result);
//关闭池对象
forkJoinPool.shutdown();
}
}转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 george_95@126.com